





Development of P2P crypto exchanges and escrow platforms
P2P cryptocurrency trading involves direct transactions between users without the participation of a classic trading engine. This format removes some of the infrastructure and regulatory restrictions, but at the same time places increased demands on security, transaction execution logic, and trust between the parties.
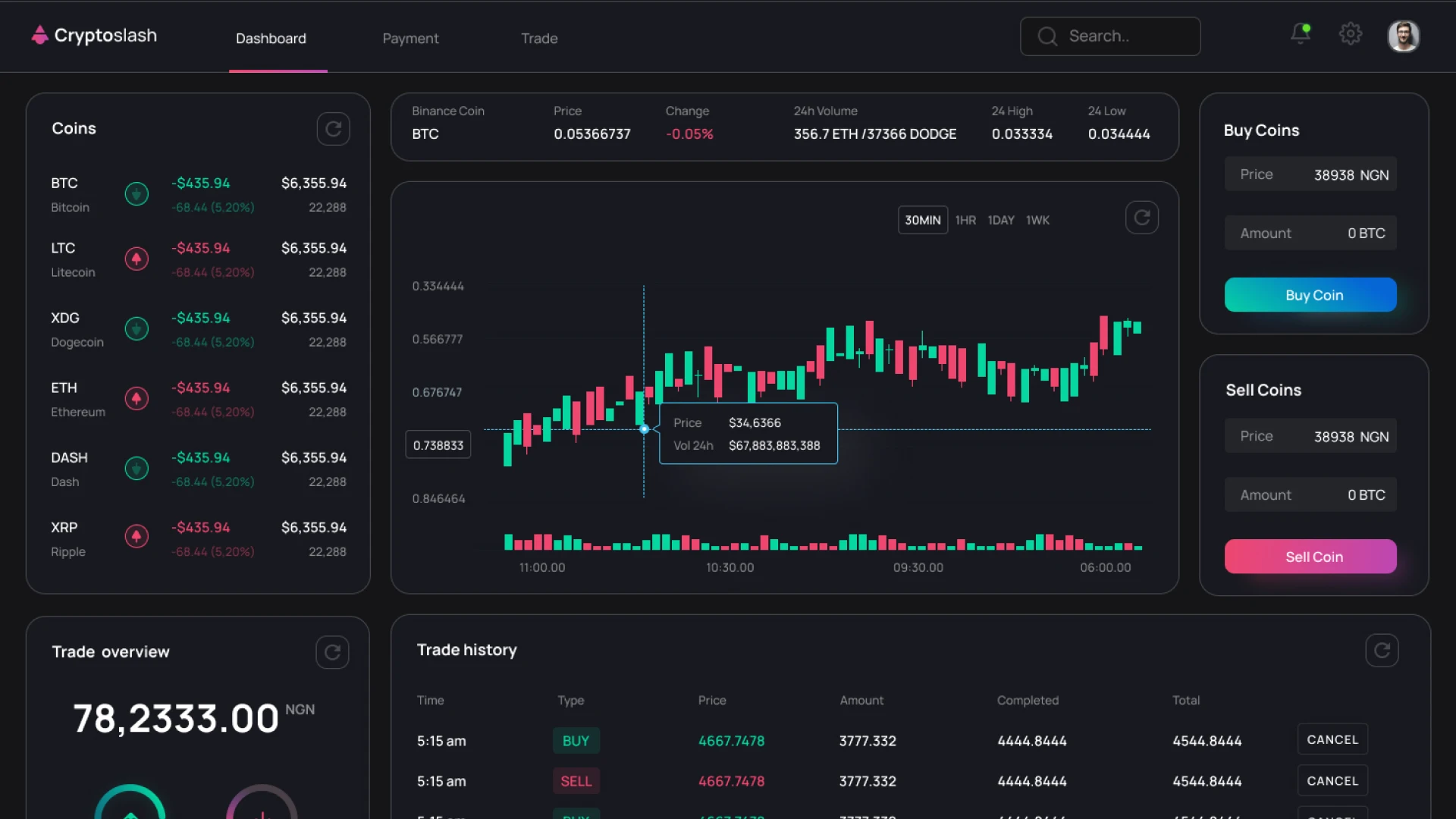
CryptonisLabs develops P2P crypto exchanges and escrow platforms in which users make transactions directly with each other, and the platform guarantees their safe execution using escrow mechanisms, KYC/AML, and an arbitration system – according to the principles used in LocalBitcoins or Binance P2P.
We are able to create not just an interface for placing ads, but a full-fledged technological infrastructure that works stably under high load conditions, eliminates the risks of fraud, and provides full control over the entire life cycle of a P2P transaction.
What is a P2P platform?
A P2P crypto exchange is a software system in which users buy and sell cryptocurrency directly among themselves, without the platform acting as a party to the transaction. Its key role is to technically guarantee the fulfillment of agreements between participants.
The security of such transactions is ensured by an escrow mechanism or smart contracts. At the time of creating a transaction, the cryptocurrency is blocked in an escrow wallet and remains there until both parties confirm the fulfillment of the terms or until an arbitration decision in the event of a dispute.
Developing a P2P crypto exchange requires a precise balance between security, user convenience, and minimizing trust in the platform as a party to the transaction.
Unlike centralized exchanges, P2P platforms:
- do not keep users' funds on the platform's balance;
- do not use a trading engine and order book;
- do not create liquidity artificially, but work with user supply.
Such solutions are especially popular in markets where fiat gateways are limited, access to classic CEXs is difficult, or a decentralized trust model based on technology rather than brand is needed. A P2P platform for crypto trading is especially effective where flexibility of terms and the absence of a trading engine are important.
Architectural examples: LocalBitcoins, Binance P2P, Paxful, OKX P2P.
How does a P2P platform differ from a classic crypto exchange and CEX?
When choosing a crypto platform format, it is important to understand that P2P solutions, classic exchangers, and centralized exchanges solve fundamentally different business tasks. They differ not only in interface, but also in architecture, level of responsibility for user funds, and regulatory burden.
The central idea of the platform
| Platform type | Who exchanges cryptocurrency? | Where are the funds stored? |
|---|---|---|
| CEX (centralized exchange) | Users trade within the platform via a trading engine and order book | Funds are stored on the exchange (custodial) |
| Exchanger (swap / exchanger) | The user exchanges cryptocurrency directly on the service at a fixed or floating rate | Funds are transferred through the service or API liquidity |
| P2P (peer-to-peer) | Users exchange directly with each other | The funds are temporarily blocked in escrow, the platform does not own them. |
This is where the key difference arises:
The P2P platform is not a counterparty to the transaction, it only guarantees its safe execution.
Level of centralization and trust
| Criterion | CEX | Exchanger | P2P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Level of centralization | Complete | Partially | Minimum |
| Who manages the funds? | Platform | Platform | Escrow / smart contract |
| Transparency of operations | Low | Medium | High (every transaction is recorded) |
| Who is trusted? | To the company | To the brand | To technology |
| Regulatory requirements | Mandatory licenses | PSP / KYC | Possibly without a license (under the escrow model) |
For business this means:
- CEX – maximum requirements for licensing and storage of funds.
- Exchanger – responsible for the rate, liquidity, and API.
- P2P – fewer legal barriers, but higher requirements for escrow and arbitration.

Main types of P2P solutions
There is a frequent request in the market for developing an alternative to LocalBitcoins with full control over the escrow logic and arbitration mechanisms. Below we will consider possible approaches to implementing such solutions.
P2P platforms can differ significantly in terms of their operating logic and business model. When designing, we always start from the specific task the system should solve, rather than from a universal template.
P2P Marketplace (classic)
The classic format of a P2P marketplace involves users creating their own ads for buying or selling cryptocurrency, selecting counterparties, and agreeing on the terms of the transaction. The platform provides escrow, chat, basic arbitration, and a rating system. A P2P crypto marketplace generates liquidity through the community, rather than an internal pool of assets.
This type scales well at the expense of users, but requires thoughtful anti-fraud logic, limits, and behavioral risk control.
Examples: LocalBitcoins, Binance P2P.
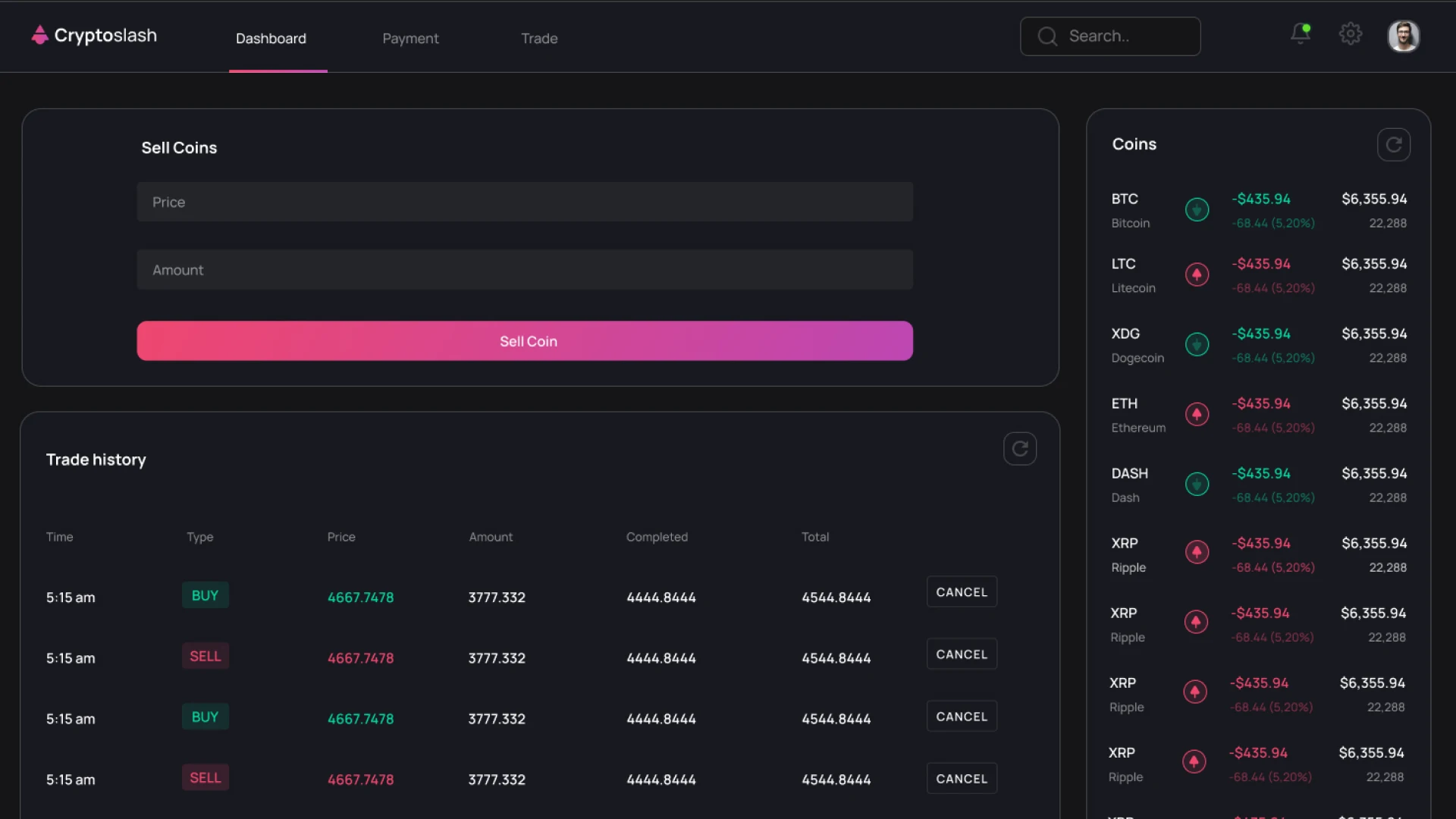
Escrow Platform
In such systems, the key element is the mechanism for blocking funds in a smart contract or escrow wallet. The logic of transaction execution is as formalized as possible, and the human factor is minimized.
This format is suitable for projects where transparency and technical verification of each operation are critically important.
Examples: Paxful, HodlHodl.
OTC P2P Hybrid
Hybrid solutions combine a P2P model with an internal brokerage or semi-automated module. Some transactions can be executed according to predefined rules, which increases the speed and manageability of the process.
This format is often used by exchanges or fintech platforms as a separate P2P direction.
Example: WhiteBIT P2P.
Telegram-P2P Bot
P2P transactions and notifications are implemented through the Telegram interface. This solution is focused on local communities, fast transactions, and minimal UX.
Despite their outward simplicity, such bots require complex server logic and a reliable escrow mechanism.
Examples: custom TON/USDT P2P bots.
Business model and sources of income
| Platform type | Basic income | Who is suitable for? |
|---|---|---|
| CEX | Trading fees, token listing, launchpad, derivatives | Large exchanges, funds, fintech corporations |
| Exchanger | Spread, exchange commission | Fintech services, payment companies |
| P2P | Transaction fee, escrow fee, arbitration | Local communities, startups, markets with restrictions |
The P2P platform allows you to start a business without having to generate your own liquidity, as it is created by the users themselves.
Key features and modules
A full-fledged P2P platform consists of two logical layers – user and administrative. Their balance directly affects the trust, security, and scalability of the business.
Functionality for users:
- creation and publication of buy or sell orders;
- filtering by currencies, countries and payment methods;
- secure chat between the parties to the transaction;
- automatic blocking of funds in the escrow wallet;
- confirmation of transaction execution and release crypto;
- account with transaction history, ratings and reviews;
- notifications via Telegram or e-mail.
These modules shape the user experience and directly affect the reuse of the platform.
Functionality for the administrator:
- centralized user and order management panel;
- arbitration module with a full history of actions;
- flexible setting of commissions and limits;
- monitoring the liquidity and status of escrow wallets;
- KYC/AML integration and reporting;
- ticket and internal message system.
It is this level that determines how manageable, secure, and viable a P2P platform is in the long term.
Integrations
A P2P platform cannot exist in isolation. Its stability, security, and user-friendliness directly depend on the quality of integrations with external services – blockchains, wallets, payment providers, and compliance systems.
CryptonisLabs designs integrations at the architecture level, rather than as additional modules “on top” of a ready-made system. This avoids bottlenecks, scaling issues, and critical failures under load.
Wallets
The platform can work with both custodial and non-custodial solutions – depending on the chosen risk and liability model.
We implement integrations with:
- BTC, USDT (ERC20, TRC20, BEP20);
- TON, ETH, BNB and other networks.
Special attention is paid to key management, access rotation, and separation of rights between services.
A P2P wallet system should ensure secure interaction between users without permanently storing funds on the platform's balance.
Blockchain API
To work with blockchains, proven providers are used:
- Infura, QuickNode;
- TON API;
- TronWeb.
We take into account speed limits, confirmation delays, mempool features, and possible forks – all of which are critical for escrow to work properly.
Payment and fiat gateways
P2P solutions often combine cryptocurrency and fiat payments. We integrate payment gateways taking into account jurisdictions, currencies and use cases:
- Cryptomus, NOWPayments;
- Mercuryo, Transak and others.
KYC/AML
Compliance is implemented not formally, but taking into account the business logic of the platform:
- Sumsub;
- ShuftiPro;
- Veriff.
It is possible to set different verification levels depending on limits, volumes, and user role.
Notification systems
To ensure prompt interaction with users, integration can be implemented with:
- Telegram Bot API;
- Twilio;
- SendGrid, etc.
Notification of deal status, arbitration, confirmation, and risks is a critical element of trust.
Solution architecture
A P2P platform is a complex multi-layered system where an architectural error can lead to loss of funds or business shutdown. That is why CryptonisLabs starts every project with architectural design, not UI or features.
A typical P2P solution architecture includes:
- Frontend (React / Next.js / Vue)
User interface optimized for quick work with orders, chats and notifications. - Backend (Node.js / Nest.js / Go)
The heart of the platform, where the business logic of transactions, state control, arbitration, and access are implemented. - Escrow Service
A separate service or smart contract responsible for blocking and unblocking funds. - Database (PostgreSQL / Redis)
Storing transaction history, logs, ratings, statuses and user actions. - KYC / AML / Arbitration Module
Compliance and dispute resolution modules tightly integrated with deal logic. - Blockchain Layer
Level of interaction with BTC, ETH, USDT, TON and other networks.
From a technical point of view, a P2P platform is simpler than a CEX, but significantly more complex than an exchanger, since all the security logic is concentrated in escrow and transaction status control.
Off-chain vs On-chain escrow
At the design stage, we always determine the optimal escrow model:
- Off-chain escrow
Funds are blocked on the server. Advantages – speed, flexibility, lower fees. Disadvantage – higher platform liability. - On-chain escrow
Blocking via smart contracts. Maximum transparency and minimum trust in the platform, but more complex logic and more expensive execution.
The choice of model depends on the market, jurisdiction, and business goals of the client.
Escrow Mechanics
A crypto escrow platform allows transactions to be executed between strangers without transferring control of funds to a centralized service. Escrow is a key element of any P2P platform. It replaces trust between strangers with a clearly defined technical logic.
The escrow process looks like this:
- After creating a transaction, the cryptocurrency is automatically locked in an escrow wallet or smart contract.
- Both parties fulfill their obligations in accordance with the terms of the agreement.
- After confirmation of execution, the funds are unblocked and transferred to the recipient.
In the event of a dispute, the agreement goes into arbitration status. The administrator gains access to:
- history of the parties' actions;
- correspondence;
- timestamps;
- transaction confirmations.
Crypto-arbitrage software in P2P systems requires detailed logging and a transparent history of the parties' actions.
For on-chain implementations, escrow logic is provided by smart contracts, digital signatures, and multi-level state checks.
Security
The P2P platform works with direct transactions between users, so any vulnerability can have financial consequences. The development of escrow smart contracts requires careful auditing, as any error directly affects user funds. That is why security in our solutions is built at the architectural level, not as an additional module.
CryptonisLabs implements a comprehensive approach to protection:
- mandatory or flexibly configurable KYC/AML verification;
- separation of hot and cold wallets;
- two-factor authentication and e-mail confirmation;
- IP filtering and monitoring of anomalous activity;
- audit of smart contracts for on-chain escrow;
- full logging of user and administrator actions.
This approach minimizes the risks of fraud, technical failures, and human errors even under high loads and platform scaling.
Additional platform features
In addition to the basic logic of P2P transactions and escrow, a modern platform should have tools that increase user engagement, stimulate liquidity, and create long-term business value.
CryptonisLabs can build in additional capabilities at the architectural design stage so that they do not look like a "superstructure", but work as part of a single system.
These opportunities include:
- Referral programs – with flexible accrual rules, anti-fraud control, and limits.
- The platform's commission model – commissions for transactions, withdrawals, or premium features.
- The rating and feedback system is one of the key tools for building trust between users in a P2P environment.
- Integration of Telegram bot or email newsletters – for notifications, confirmation of actions, marketing newsletters and, if necessary, performing actions without logging into the web interface.
- Mobile version or PWA – for markets where mobile access is the main channel of interaction.
Such additional features directly impact user retention and platform scaling without increasing operational costs.
What distinguishes CryptonisLabs' approach?
As an alternative to Binance P2P, a custom platform allows you to fully control fees, access rules, and arbitrage mechanics. Developing a P2P crypto exchange or escrow platform requires not only knowledge of the technology, but also an understanding of market risks, user behavior, and regulatory restrictions.
CryptonisLabs has been working with P2P models, escrow and arbitration systems for many years, creating solutions for different jurisdictions and usage scenarios.
Key characteristics of the CryptonisLabs approach:
- experience in developing P2P exchanges and escrow systems, not universal “scripts”;
- deep expertise in smart contracts and off-chain escrow architectures;
- working with Ethereum, BNB, TON, Tron and Bitcoin at the protocol and API level;
- ready-made integrations with KYC/AML and payment gateways;
- white-label solutions under the client's brand;
- building APIs and Telegram bots for partners and communities;
- post-launch support and optimization, taking into account market changes.
Our approach is engineering responsibility for the result, not just implementing functions according to the specifications. The ready-made script of a P2P crypto exchange does not take into account the specifics of the market, so we design individual solutions from scratch.
Launching a turnkey P2P solution
If you are considering launching a P2P crypto exchange or escrow platform, the key factor for success is not a set of features, but a correctly designed architecture – escrow logic, transaction status control, arbitrage, and security.
CryptonisLabs develops turnkey P2P platforms – from formalizing business requirements and architectural design to stable operation in production, taking into account loads, regulatory restrictions, and user behavior.
As a first step, we offer an architectural consultation, during which:
- we determine the optimal P2P model for your market;
- choose an escrow approach (on-chain or off-chain);
- We outline key risks and limitations before development.
FAQ
-
What responsibility does the platform bear for users' funds?
In the P2P model, the platform is not a counterparty to transactions and does not own users' funds. Its responsibility is to correctly implement escrow logic, control transaction states, and arbitrage. The level of responsibility directly depends on the chosen escrow model (on-chain or off-chain).
-
On-chain or off-chain escrow – which is safer for business?
On-chain escrow reduces trust in the platform and increases transparency, but is more complex and expensive to implement. Off-chain escrow provides greater flexibility and lower fees, but requires increased control and accountability of the platform. The choice is always made taking into account regulatory and business constraints.
-
What are the main risks when launching a P2P platform and how are they controlled?
Key risks include errors in escrow logic, fraudulent scenarios, weak arbitrage, and uncontrolled user actions. These are controlled through architectural design, logging of all actions, clear transaction scenarios, KYC/AML, and a multi-layered security system.
-
Is it mandatory to implement KYC/AML and at what stage?
KYC/AML is not always required for all users. A multi-tiered model is often used, where verification depends on limits, transaction volumes, or user role. This solution allows for a balance between compliance and convenience.
-
Is it possible to scale the platform without increasing operating costs?
Yes, with the right architecture. Automated escrow, clear arbitration logic, integrated alerts and analytics allow the platform to scale without a proportional increase in the operations team.
-
How long does it take to develop a turnkey P2P platform?
The timing depends on the complexity of the model, the number of integrations, and the escrow approach. On average, a full-fledged project includes the analytics, architecture, development, testing, and launch stages, which take from several months to a year.
-
What is the best place to start before launching development?
The first step is an architectural consultation. It allows you to determine the optimal P2P model, escrow approach, key risks, and requirements before development begins, reducing the likelihood of costly mistakes in the future.